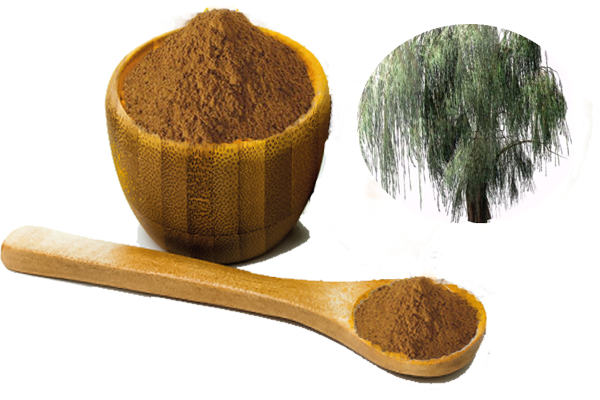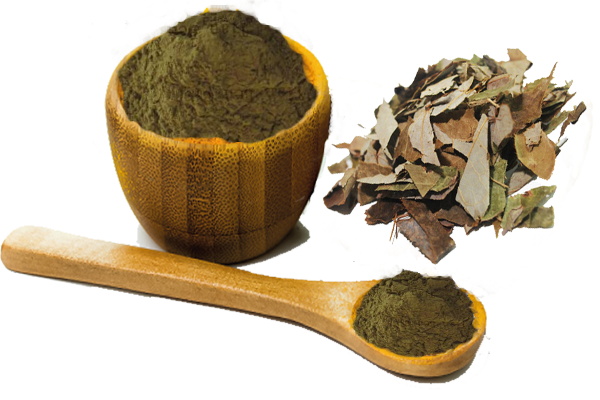
White Willow Bark Extract
White Willow Bark Extract
White Willow Bark Extract Salicin 15%, 50%,98%, , concentrated extract 10:1, 20:1, 30:1 with analysis meets the EP, USP, JP, CP.....
White Willow Bark Extract Powder / Salicin 15% ~98%
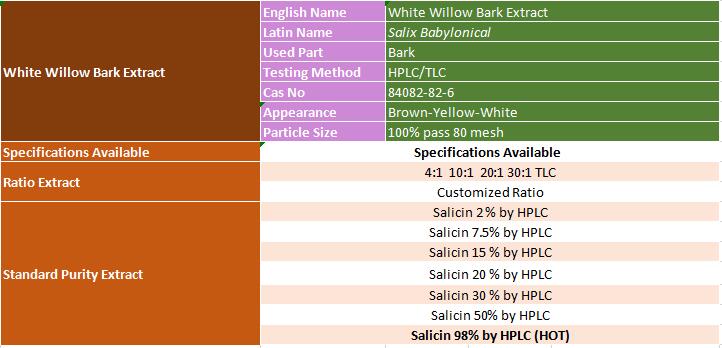
white willow bark extract specification
What’s the White Willow Bark Extract
Willow bark is the bark from several varieties of the willow tree, including white willow or European willow, black willow or pussy willow, crack willow, purple willow, and others. The bark is used to make medicine.
Willow bark acts a lot like aspirin, so it is used for pain, including headache, muscle or joint pain, menstrual cramps, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), osteoarthritis, gout, and a disease of the spine called ankylosing spondylitis.
Willow bark’s pain relieving potential has been recognized throughout history. Willow bark was commonly used during the time of Hippocrates, when people were advised to chew on the bark to relieve pain and fever.Willow bark is also used for the common cold, flu, and weight loss.
Salicin, the active ingredient in willow bark, seems to have contributed to the death of the composer, Ludwig von Beethoven. Apparently, Beethoven ingested large amounts of salicin before he died. His autopsy report is the first recorded case of a particular type of kidney damage that can be caused by salicin.
The History for White Willow Bark Extract used in Medicine
The medicinal use of willow dates back 6,000 years. Ancient civilizations used willow tree extracts to treat pain, inflammation, and musculoskeletal conditions. Assyrian clay tablets excavated by archaeologists document these uses of willow and also in treating fever. Egyptians used willow to treat joint pain and inflammatory conditions associated with wounds. Chinese civilizations used willow to treat fever, pain, colds, hemorrhages, goiter, and rheumatic fever and applied willow as an antiseptic for wounds and abscesses. Physicians of ancient Greece, including Dioscorides who wrote the precursor to all modern pharmacopeias, prescribed willow for its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties.
North American willows have also been used in folk medicine. Most of the European medicinal willows were introduced to the Americas and escaped cultivation. In the late 19th century, salicylic acid was widely used in place of willow bark, and its derivative, aspirin, was discovered to be less irritating to the mouth and stomach.
Chemistry for White Willow Bark Extract
Salicylate derivatives are the primary medicinal constituents of willow bark. While small amounts of salicylic acid can be detected in most species, the principle salicylates of S. alba are the phenolic ester glycoside salicortin and glycoside salicin, its acid hydrolysis product. Although salicin is considered the major active constituent, there is research interest in the anticancer activity of polyphenols and flavonoids in willow bark.
Salicin is hydrolyzed in the intestine to saligenin (o-hydroxybenzyl alcohol), which is absorbed and then oxidized to salicylic acid. Salicortin and other related salicylates are chemically unstable (ie, to boiling water for teas)and to avoid the loss of these compounds, careful drying of the bark is required. Extraction protocols, used to avoid decomposition of the native glycosides, have been developed. Most standards for medicinal willow bark require salicylates to be present in more than 1% of dry weight, but are difficult to achieve with many species. This has stimulated surveys of the salicylate content of many other species of Salix as well as aspen (Populus), which also contains salicylates.While the leaves generally contain lower concentrations of salicylates than the bark, several species contain medicinally useful quantities of salicylates in their leaves.
A number of analytical approaches have been used to quantify salicylates in willows, including spectrophotometry, thin-layer chromatography (TLC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) after enzymatic deglycosylation, capillary electrophoresis, and an electrochemical method known as square wave voltammetry.A method using gas chromatography of silyl derivatives of salicylates gave results comparable to those of HPLC.An HPLC method was used to compare the salicylate content of different cultivated clones of Salix myrsinifolia grown in a single location.
Benefits Function of White Willow Bark Extract
Relieves Pain
Due to its rich blend of antioxidants and organic compounds, willow bark functions as a very successful analgesic. [2] For thousands of years, it has been traditionally used to relieve pain from injuries and illness, with great success. In fact, more than 2,500 years ago, the earliest recorded use of an herb was of willow bark, in Chinese traditional medicine. Although it was mentioned in older texts dating back to the Egyptians, this was the first documented use of willow bark for pain relief!
Anti-inflammatory Properties
Inflammation takes on many different forms within our body. If you are looking to eliminate the inflammation in your respiratory tracts, gastrointestinal system, or joints, then willow bark can quickly soothe your symptoms. [3] If you prepare a decoction or a tea of this bark, you will feel the inflammation and topical pain from arthritis, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gout, and other conditions disappear.
Reduces Fever
One of the most important anti-inflammatory properties of willow bark is in the reduction of fevers. Fevers are a symptom of an infection in the body, but reducing a fever or breaking it is important to speed up the healing process and get the organs working normally again. [4] It has been used to treat fevers for thousands of years.
Eases Menstruation
For many women who suffer from abnormally heavy periods or severe menstrual symptoms, taking a small glass of willow bark can do wonders for everything from period pains and cramping to mood swings and unnecessary stress hormones in the body. [5] Its relaxing characteristics are particularly good in these circumstances, as they can help re-balance hormones in a woman’s body.
Soothes Stomach Disorders
The high content of tannins can help soothe [6] the stomach and prevent gastrointestinal distress during other illnesses or periods of a weakened immune system. While willow bark can be slow-acting, its effects can be long-lasting, making it an effective herbal remedy to occasionally add to your health regimen, but it should not be consumed daily unless advised by a doctor or trained herbalist.
Weight Loss
Many people turn to willow bark to enhance their weight loss efforts, namely because the herb combines so well with other fat-burning and metabolism-boosting substances. [7] It can intensify the effects of these herbs in a healthy way, thereby increasing their efficacy and improving your results even further.
Skin Care
The appearance of the skin is very important for many people, and the high content of antioxidant compounds found in willow bark can have a major impact on the health of the skin. Whether applied topically or consumed, willow bark can increase blood flow to the skin due to its antioxidants, while also reducing the appearance of wrinkles and age marks. Furthermore, it can eliminate inflammation in the skin and ease the pain of insect bites and irritation.
Interactions and Depletions
Because willow bark contains salicylates, it might interact with a number of drugs and herbs. Talk to your doctor before taking willow bark if you take any other medications, herbs, or supplements.
Willow bark may interact with any of the following:
Anticoagulants (blood-thinning medications): Willow bark may strengthen the effects of drugs and herbs with blood-thinning properties, and increase the risk of bleeding.
Beta blockers: including Atenolol (Tenormin), Metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol-XL), Propranolol (Inderal, Inderal LA). Willow bark may make these drugs less effective.
Diuretics (water pills): Willow bark may make these drugs less effective.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: including ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve). Taking willow bark with these drugs may increase risk of stomach bleeding.
Methotrexate and phenytoin (Dilantin): Willow bark may increase levels of these drugs in the body, resulting in toxic levels.
PS: We also provide more various health functional herbs extract. For more exact information,please check here

















